During Acetyl Coa Formation and the Citric Acid Cycle
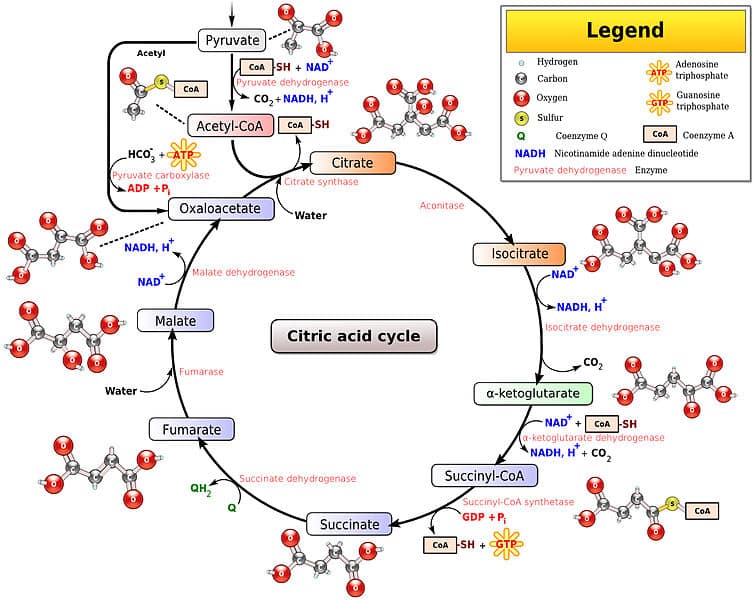
Acetyl CoA transfers its acetyl group to oxaloacetate to form citrate and begin the citric acid cycle. They release the CoA group and form a 6C molecule called Citrate.
The Tca Cycle Steps Krebs Cycle Teachmephysiology
The citric acid cycle.

. How many ATP are produced from 1 pyruvate. Drag the labels from the. Acetyl-CoA acetyl coenzyme A is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
Through catabolism of sugars fats and proteins the two-carbon organic. The release of carbon dioxide is coupled with the reduction of NAD to NADH in the citric acid cycle. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl joins with a four-carbon molecule oxaloacetate releasing the group and forming a six-carbon molecule called citrate.
Coenzyme A CoASH or CoA consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid B5 through. It is produced by the oxidation of pyruvate which is the end product of glycolysis. Acetyl CoAs most important steps are the decarboxylation 1 and the addition of coenzyme A 3.
In carbohydrate metabolism acetyl CoA is the link between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Acetyl-CoA then enters in the. Hydrochloric acid HCL is added during the titration of ascorbic acid because the reaction should.
Why is it called the citric acid cycle. The two main purposes of the citric acid cycle are. This requires perfusing with.
The resumed steps of the Citric acid cycle are as follows 1 Acetyl CoA joins an oxaloacetate molecule which is a 4C molecule. The citric acid cycle is a key metabolic pathway that connects carbohydrate fat and protein metabolismThe reactions of the cycle are carried out by eight enzymes that completely oxidize acetate a two carbon molecule in the form of acetyl-CoA into two molecules each of carbon dioxide and water. Drag the labels from the left which represent numbers of carbon atoms onto the diagram to identify the number of carbon atoms in.
From the last step glycolsis pyruvate was made. The table below provides data for the enthalpy and entropy of formation of compounds A and B at. During the first step of cellular respiration glycolysis a 6-carbon glucose molecule is split into two 3-carbon molecules called pyruvate.
A single molecule of acetyl-CoA will produce 10 to 12 molecules of ATP. Through a series of steps citrate is oxidized releasing two carbon dioxide molecules for. The carbon for de novo fatty acid synthesis is largely from TCA cycle derived citrate.
A synthesis of citrate and gluconeogenesis. Acetyl-CoA is a metabolite derived from glucose fatty acid and amino acid catabolism. Through a series of steps citrate is oxidized releasing two carbon dioxide molecules for each acetyl group fed into the cycle.
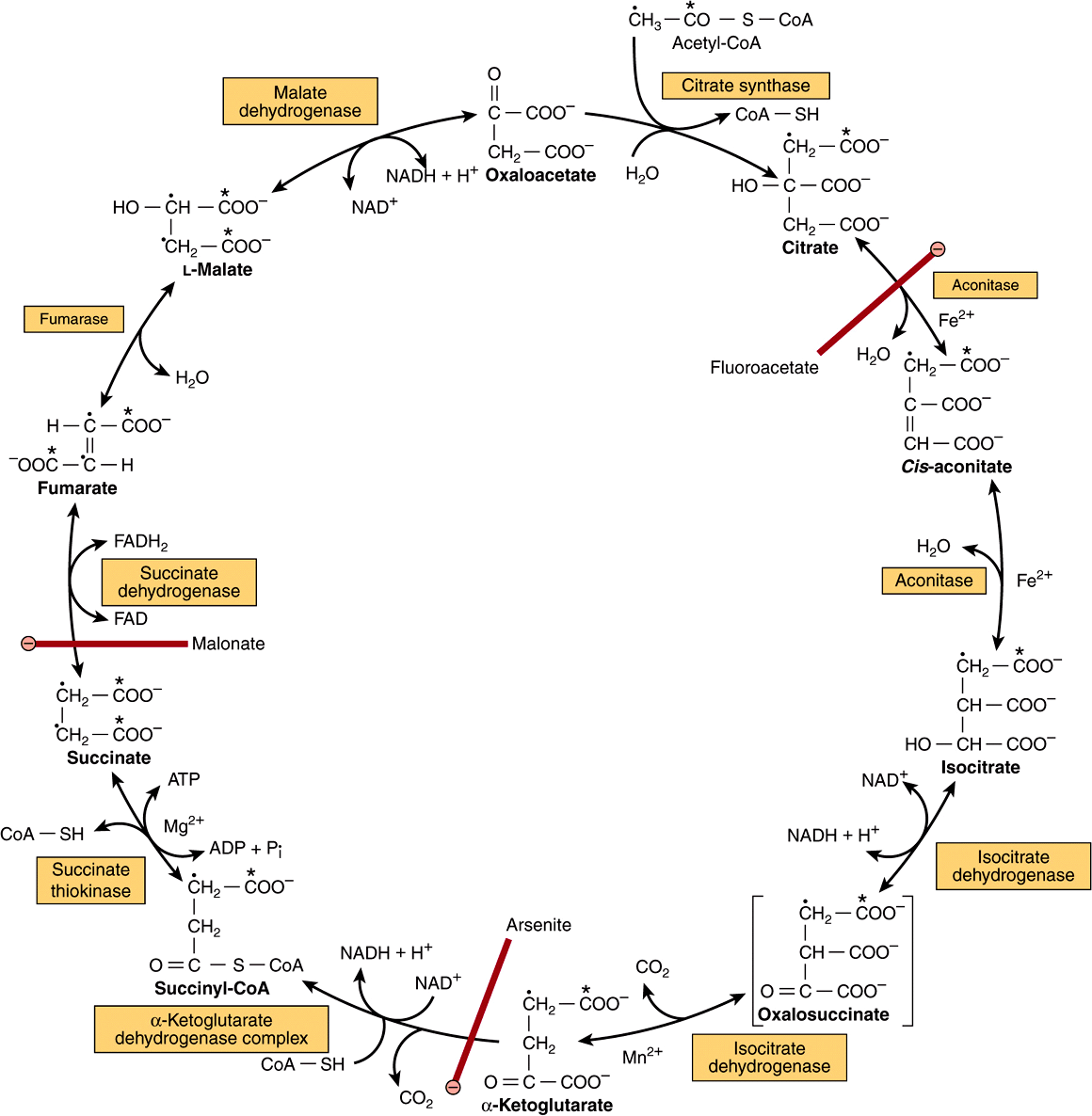
In the citric acid cycle the acetyl group from acetyl CoA is attached to a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon citrate molecule. The resulting citrate is then converted to cis-aconitate and then isocitrate via the enzyme aconitase. Acetil CoA Oxalacetato Citrato CoA group 2 Citrate turns into an isomere Isocitrate.
Acetyl-CoA is the reactant needed in the citric acid cycle. Acetyl-CoA is generated either by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate from glycolysis which occurs in mitochondrial matrix by oxidation of long-chain fatty acids or by oxidative degradation of certain amino acids. The creation of this enzyme is a crucial step in the cellular respiration cycle.
Up to 24 cash back The initiator of the citric acid cycle is acetyl co-enzyme A so its formation is important. These pyruvate molecules must by oxidized and converted to acetyl-CoA which will. During acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle all of the carbon atoms that enter cellular respiration in the glucose molecule are released in the rack the carbon-containing compounds that play a role in these two stages.
In the citric acid cycle the acetyl group from acetyl CoA is attached to a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon citrate molecule. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle Krebs cycle to be oxidized for energy production. The citric acid cycle.
During glycolysis glucose is broken down into two three-carbon molecules of pyruvate. Use this diagram to track the carbon-containing compounds that play a role in these two stages. Pyruvic acid CoA NAD --- acetyl CoA NADH H CO 2.
This acetyl CoA goes into the citric acid cycle and then all of the NADH and FADH2 produced are covnerted to ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. The citric acid cycle begins with acetyl-CoA transferring its two-carbon acetyl group to the four-carbon acceptor compound oxaloacetate to form a six-carbon compound citrate through the enzyme citrate synthase. The mitochondrial pyruvate dehydrogenase complex then catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to produce acetyl-CoA a two-carbon acetyl unit that is ligated to the acyl-group.
Cytoplasmic malonyl-CoA is generated by carboxylation of acetyl-CoA via highly regulated acetyl-CoA carboxylase ACC and utilized by Fatty Acid Synthase FASN to generate palmitate. The overall formation reaction of acetyl CoA may be represented as. B degradation of acetyl-CoA to produce energy and to supply precursors for anabolism.
We present a strategy for simultaneous assessment of the relative contributions of anaplerotic pyruvate carboxylation pyruvate decarboxylation and fatty acid oxidation to citrate formation in the perfused rat heart. The next step is the formation of acetyl coenzyme A acetyl CoA which is the initiator of the citric acid cycle. Part A-Carbon atoms in acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cyclo During acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle all of the carbon atoms that enter cellular respiration in the glucose molecule are released in the form of Co Use this diagram to track the carbon-containing compounds that play a role in those two stages.
During acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle all of the carbon atoms that enter cellular respiration in the glucose molecule are released in the form of CO2. 15 ATPs So in total 15 ATPs are produced from one molecule of pyruvate. In the second step citrate is converted into its isomer isocitrate.
Where the acetyl group has been released from acetyl-CoA the remaining coenzyme A aids in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA before re-entering the citric acid cycle. Fatty acid synthesis therefore is an efficient method to store carbohydrates. The name citric acid cycle is derived from the first product generated by the sequence of conversions ie citric acid.
The citric acid cycle constantly forms and regenerates coenzyme A and acetyl-CoA.

The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy

5 6c Acetyl Coa And The Citric Acid Cycle Biology Libretexts
The Citric Acid Cycle The Catabolism Of Acetyl Coa Basicmedical Key

No comments for "During Acetyl Coa Formation and the Citric Acid Cycle"
Post a Comment